This post is about the estimation land surface temperature using Landsat Satellite and ASTER Satellite images. In this tutorial we are going to use a land cover classification for the definition of surface emissivity, which is required for the calculation of the land surface temperature. It is assumed that one has the basic knowledge of SCP and Basic Tutorials.
Our study area will be Paris (France), an area covered by urban surfaces, vegetation and agricultural fields.
Before downloading data, please watch the following video that illustrates the study area and provides very useful information about thermal infrared images, and their application (footage courtesy of European Space Agency/ESA). Also, a brief description of the area that we are going to classify is available here .
The thermal infrared band is particularly useful for assessing the temperature difference between the city and the surrounding rural areas, and studying the urban heat island phenomenon. We are going to use Landsat and ASTER images for the estimation of land surface temperature. For more information about the conversion of raster bands please read Conversion to At-Satellite Brightness Temperature. Following the video of this tutorial.
1. Data Download and Conversion
We are going to download the Landsat 8 image acquired in 2015 (image ID =LC81990262015270LGN00, data available from the U.S. Geological Survey).Start a new QGIS project. Open the tab Download images clicking the button
 in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Select the tab Landsat download.
in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Select the tab Landsat download.In Login https://ers.cr.usgs.gov/ you should enter the user name and password for accessing data (free registration at USGS EROS is required) in User and Password. However, in this case login should not be required because this Landsat 8 image is available directly from the Amazon Web Services (AWS) .
In Search area enter:
- UL X (Lon): 2
- UL Y (Lat): 49
- LR X (Lon): 2.5
- LR Y (Lat): 48.8
TIP : In general it is possible to define the area coordinates clicking the button
 and drawing a rectangle in the map.
and drawing a rectangle in the map.
L8 OLI/TIRS from the list Satellites and set the acquisition date:- Date from: 2015-09-27
- to: 2015-09-27
 and after a few seconds the image will be listed in the
and after a few seconds the image will be listed in the Image list.In the result table, click the item
LC81990262015270LGN00 in the field ImageID, and click the button  . A preview will be downloaded and displayed in the map, which is useful for assessing the quality of the image and the cloud cover.
. A preview will be downloaded and displayed in the map, which is useful for assessing the quality of the image and the cloud cover.
Image preview
- 2 = Blue
- 3 = Green
- 4 = Red
- 5 = Near-Infrared
- 6 = Short Wavelength Infrared 1
- 7 = Short Wavelength Infrared 2
- 10 = Thermal Infrared (TIRS) 1
The checkbox
 Preprocess images allows for the automatic conversion of bands after the download, according to the settings defined in Landsat; we are going to apply the DOS1 Correction. Bands from 2 to 7 will be converted to reflectance and band 10 will be converted to At-Satellite Brightness Temperature. Open the tab Landsat, check
Preprocess images allows for the automatic conversion of bands after the download, according to the settings defined in Landsat; we are going to apply the DOS1 Correction. Bands from 2 to 7 will be converted to reflectance and band 10 will be converted to At-Satellite Brightness Temperature. Open the tab Landsat, check  Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction and uncheck
Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction and uncheck  Create Band set and use Band set tools (we are going to create the Band set after the clip of the image to study area).
Create Band set and use Band set tools (we are going to create the Band set after the clip of the image to study area).In order to start the download and conversion process, open the tab Landsat download, click the button
 and select the directory where converted bands are saved (e.g.
and select the directory where converted bands are saved (e.g. Desktop). After a few minutes, converted bands are loaded and displayed (file name starts with RT_).2. Clip to Study Area
We are going to clip the Landsat images to our study area.Open the tab Preprocessing clicking the button
 in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Select the tab Clip multiple rasters and click the button
in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Select the tab Clip multiple rasters and click the button  to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Click the button
to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Click the button  to select all the rasters to be clipped, and in Clip coordinates type the following values:
to select all the rasters to be clipped, and in Clip coordinates type the following values:- UL X: 402705
- UL Y: 5461065
- LR X: 480824
- LR Y: 5381535
Now click the button
 and select the directory where clipped bands are saved (e.g.
and select the directory where clipped bands are saved (e.g. Desktop). Clipped bands have the prefix clip_ and will be automatically loaded and displayed. We can remove the bands whose names start with RT_ from QGIS layers.
Clipped bands
3. Land Cover Classification
Now we need to classify land cover, which will be used later for the creation of the emissivity raster. For detailed instructions about the classification process please see Tutorial 2: Land Cover Classification of Sentinel-2 Images.We are going to use the following Macroclass IDs (see Classes and Macroclasses).
Macroclasses
| Macroclass name | Macroclass ID |
|---|---|
| Water | 1 |
| Built-up | 2 |
| Vegetation | 3 |
| Bare soil | 4 |
Open the tab Band set clicking the button
 and define the Landsat 8 Band set using clipped bands from 2 to 7 (excluding band 10).
and define the Landsat 8 Band set using clipped bands from 2 to 7 (excluding band 10).In the SCP dock click the button
 , define a file name for the Training input. In the list RGB= of Working toolbar select
, define a file name for the Training input. In the list RGB= of Working toolbar select 4-3-2 to display a false color composite corresponding to the bands: Near-Infrared, Red, and Green (see Color Composite).
Color composite
After the creation of several ROIs for each land cover class, we can perform the classification of the whole image (see Tutorial 2: Land Cover Classification of Sentinel-2 Images). After setting the colors of MC ID (in the tab Macroclasses of the SCP dock), in the tab Classification algorithm check the option
 MC ID to use Macroclass IDs and select the classification algorithm Maximum Likelihood.
MC ID to use Macroclass IDs and select the classification algorithm Maximum Likelihood.Then, open the tab Classification output, click the button
 and define the name of the classification output.
and define the name of the classification output.
Land cover classification
4. Reclassification of Land Cover Classification to Emissivity Values
Now we are going to reclassify the classification raster using the land surface emissivity values. The emissivity (e) values for the land cover classes are provided in the following table (values used in this tutorial are only indicative, because emissivity of every material should be obtained from field survey):Emissivity values
| Land surface | Emissivity e |
|---|---|
| Water | 0.98 |
| Built-up | 0.94 |
| Vegetation | 0.98 |
| Bare soil | 0.93 |
Open the tab Postprocessing clicking the button
 in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Select the tab Reclassification and click the button
in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Select the tab Reclassification and click the button  to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Select the classification raster from the list.
to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Select the classification raster from the list.Click the button
 to add 4 rows to the table Values. In this table, set the old value (the Macroclass ID of the classification) and the new value (the corresponding emissivity e ) for every land cover class. Uncheck the checkbox
to add 4 rows to the table Values. In this table, set the old value (the Macroclass ID of the classification) and the new value (the corresponding emissivity e ) for every land cover class. Uncheck the checkbox  Use code from Signature list, click the button
Use code from Signature list, click the button  and define the name of the output raster (e.g.
and define the name of the output raster (e.g. emissivity.tif).
Reclassification
This is the emissivity raster, where each pixel has the emissivity value that we have defined for the respective land cover class.
Emissivity raster
5. Conversion from At-Satellite Temperature to Land Surface Temperature
Now we are ready to convert the At-Satellite Brightness Temperature to Land Surface Temperature, using the following equation (see Estimation of Land Surface Temperature):- = wavelength of emitted radiance
- m K = 14388 µm K
- = Planck’s constant = J s
- = Boltzmann constant = J/K
- = velocity of light = m/s
Center wavelength of Landsat bands
| Satellite | Band | |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat 4, 5, and 7 | 6 | 11.45 |
| Landsat 8 | 10 | 10.8 |
| Landsat 8 | 11 | 12 |
Open the tab Band calc clicking the button
 in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Click the button
in the SCP menu, or the SCP Tools, or the SCP dock. Click the button  to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. We have used band 10 of Landsat 8, therefore in the Expression type the equation for conversion adapted to our rasters:
to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. We have used band 10 of Landsat 8, therefore in the Expression type the equation for conversion adapted to our rasters:"clip_RT_LC81990262015270LGN00_B10.tif" / ( 1 + ( 10.8 * "clip_RT_LC81990262015270LGN00_B10.tif" / 14388 ) * ln("emissivity.tif") )
Click the button
 and define the name of the output raster (e.g.
and define the name of the output raster (e.g. surface_temperature.tif). After the calculation, the Land Surface Temperature (in kelvin) will be loaded, and we can change the layer style. In addition, in the tab Band calc we can calculate the temperature in Celsius with the expression:"surface_temperature.tif" - 273.15
We can notice that the urban area and uncultivated land have the highest temperatures, while vegetation has the lowest temperature. The aim of this tutorial is to describe a methodology for the estimation of surface temperature using open source programs and free images. It is worth highlighting that in order to achieve more accurate results, one should perform field survey for improving the land cover classification and the estimation of surface emissivities.
In addition to Landsat, we are going to use an ASTER image and use the same methodology for the estimation of Land Surface Temperature.
6. Data Download and Conversion of ASTER Image
Open the tab Download images and select the tab ASTER download.In Login https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov enter the user name and password required for accessing data (free registration at EOSDIS Earthdata is required) in User and Password. The ASTER L1T data products are retrieved from the online Data Pool, courtesy of the NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC), USGS/Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota,https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/data_access/data_pool.
In Search area enter:
- UL X (Lon): 2
- UL Y (Lat): 49
- LR X (Lon): 2.5
- LR Y (Lat): 48.8
- Date from: 2000-08-24
- to: 2000-08-24
 and after a few seconds the image will be listed in the
and after a few seconds the image will be listed in the Image list.In the result table, click the item
AST_L1T_00308242000111313_20150411071856_3805 in the field ImageID, and click the button  . A preview will be downloaded and displayed in the map, which is useful for assessing the quality of the image and the cloud cover.
. A preview will be downloaded and displayed in the map, which is useful for assessing the quality of the image and the cloud cover.As we did for Landsat, we are going to apply the DOS1 Correction. The checkbox
 Preprocess images allows for the automatic conversion of bands after the download, according to the settings defined in ASTER. Bands from 1 to 9 will be converted to reflectance and bands from 10 to 14 will be converted to At-Satellite Brightness Temperature.
Preprocess images allows for the automatic conversion of bands after the download, according to the settings defined in ASTER. Bands from 1 to 9 will be converted to reflectance and bands from 10 to 14 will be converted to At-Satellite Brightness Temperature.Open the tab ASTER, check
 Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction and leave checked
Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction and leave checked  Create Band set and use Band set tools (this is useful to automatiacally create a Band set, which is required for the next step).
Create Band set and use Band set tools (this is useful to automatiacally create a Band set, which is required for the next step).In order to start the download and conversion process, open the tab ASTER download, click the button
 and select the directory where converted bands are saved (e.g.
and select the directory where converted bands are saved (e.g. Desktop). After a few minutes, converted bands are loaded and displayed (file name starts with RT_).7. Clip to Study Area of ASTER image
We are going to clip the ASTER images to our study area, because bands are not aligned at the border.Open the tab Preprocessing clicking the button
 . Select the tab Clip multiple rasters and click the button
. Select the tab Clip multiple rasters and click the button  to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Band set`Click the button |select_all| to select all the rasters to be clipped, and check |checkbox| :guilabel:`Use temporary ROI for clipping. Now, we can draw a manual ROI (because a Band set is already defined, see ROI creation) about the same shape of the ASTER image, about 20 pixels within the border thereof (in order to align the border of all the bands).
to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Band set`Click the button |select_all| to select all the rasters to be clipped, and check |checkbox| :guilabel:`Use temporary ROI for clipping. Now, we can draw a manual ROI (because a Band set is already defined, see ROI creation) about the same shape of the ASTER image, about 20 pixels within the border thereof (in order to align the border of all the bands).Now click the button
 and select the directory where clipped bands are saved (e.g.
and select the directory where clipped bands are saved (e.g. Desktop). Clipped bands have the prefix clip_ and will be automatically loaded and displayed. We can remove the bands whose names start with RT_ from QGIS layers.8. Land Cover Classification of ASTER Image
Using the same Macroclass IDs used for Landsat, we are going to classify the ASTER image.Open the tab Band set clicking the button
 . Click tha button
. Click tha button  to clear all bands from Band set and define the ASTER Band set using the clipped bands from 1 to 9.
to clear all bands from Band set and define the ASTER Band set using the clipped bands from 1 to 9.In the SCP dock click the button
 , define a file name for the Training input (e.g.
, define a file name for the Training input (e.g. training_ASTER). Clear the table ROI Signature list highlighting all the spectral signatures created previously for Landsat and clicking the button  .
.In the list RGB= of Working toolbar select
3-2-1 to display a false color composite corresponding to the bands: Near-Infrared, Red, and Green (see Color Composite).After the creation of several ROIs for each land cover class, we can perform the classification of the whole image. After setting the colors of MC ID (in the tab Macroclasses of the SCP dock), in the tab Classification algorithm check the option
 MC ID to use Macroclass IDs and select the classification algorithm Maximum Likelihood. Then, open the tab Classification output, click the button
MC ID to use Macroclass IDs and select the classification algorithm Maximum Likelihood. Then, open the tab Classification output, click the button  and define the name of the classification output (e.g.
and define the name of the classification output (e.g. classification_aster.tif).9. Reclassification of Land Cover Classification to Emissivity Values of ASTER Image
Now we are going to reclassify the classification raster using the same land surface emissivity values used for Landsat.Open the tab Postprocessing clicking the button
 . Select the tab Reclassification and click the button
. Select the tab Reclassification and click the button  to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Select the classification raster from the list.
to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters. Select the classification raster from the list.Click the button
 to add 4 rows to the table Values. In this table, set the old value (the Macroclass ID of the classification) and the new value (the corresponding emissivity e ) for every land cover class. Uncheck the checkbox
to add 4 rows to the table Values. In this table, set the old value (the Macroclass ID of the classification) and the new value (the corresponding emissivity e ) for every land cover class. Uncheck the checkbox  Use code from Signature list, click the button
Use code from Signature list, click the button  and define the name of the output raster (e.g.
and define the name of the output raster (e.g. emissivity_aster.tif).
ASTER reclassification
10. Conversion from At Satellite Temperature to Land Surface Temperature of ASTER Image
We can convert the At-Satellite Brightness Temperature to Land Surface Temperature, using the same equation used for Landsat (see Estimation of Land Surface Temperature).The values of for ASTER bands are listed in the following table.
Center wavelength of ASTER bands
| Satellite | Band | |
|---|---|---|
| ASTER | 10 | 8.3 |
| ASTER | 11 | 8.65 |
| ASTER | 12 | 9.1 |
| ASTER | 13 | 10.6 |
| ASTER | 14 | 11.3 |
We are going to use ASTER band 13 that has a value very similar to the Landsat band 10.
Open the tab Band calc clicking the button
 . Click the button
. Click the button  to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters, and in the Expression type equation for conversion adapted to our rasters:
to refresh the layer list and show the loaded rasters, and in the Expression type equation for conversion adapted to our rasters:"clip_RT_AST_L1T_00308242000111313_20150411071856_3805_13.tif" / ( 1 + ( 10.6 * "clip_RT_AST_L1T_00308242000111313_20150411071856_3805_13.tif" / 14388 ) * ln("emissivity_aster.tif") )
Click the button
 and define the name of the output raster (e.g.
and define the name of the output raster (e.g. surface_temperature_aster.tif). After the calculation, the Land Surface Temperature (in kelvin) will be loaded, and we can change the layer style. In addition, in the tab Band calc we can calculate the temperature in Celsius with the expression:"surface_temperature_aster.tif" - 273.15
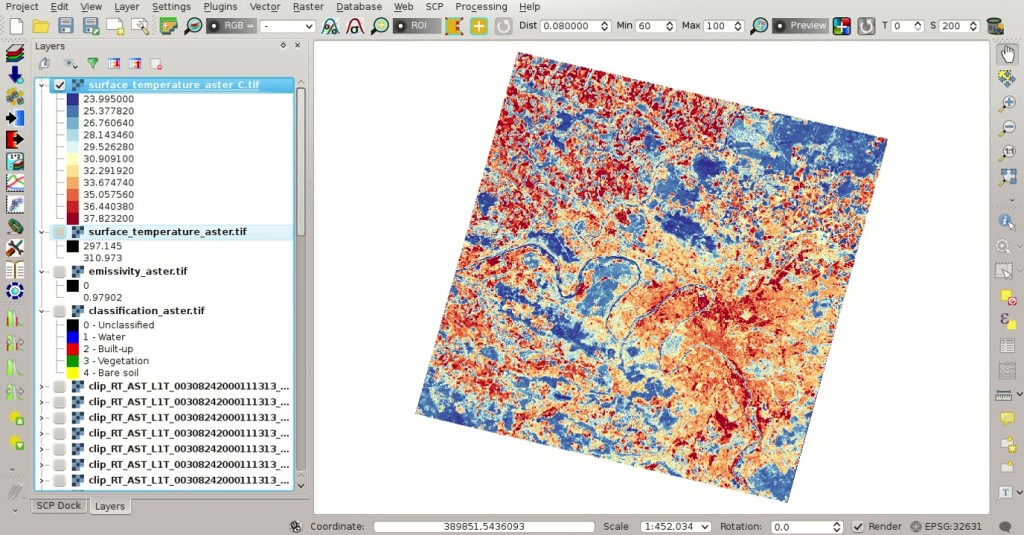
The ASTER image shows temperature values higher than the Landsat image. For instance, we could perform the difference between the two surface temperature rasters (Landsat and ASTER) to assess the variation of temperature. However, we should notice that the two images were acquired in different months (Landsat on 27-09-2015 and ASTER on 24-08-2000).
The large availability of Landsat and ASTER images for the past decades allows for the reliable monitoring of land cover and surface temperature. Nevertheless, cloud cover can limit the number of images that can be effectively used.
This tutorial illustrated a methodology of temperature estimation using these satellite images and open source programs. One should always consider that the estimation accuracy depends on several factors, such as the thematic and spatial accuracy of land cover classifications and the reliability of the emissivity values. Estimation errors can be of 1 K or even more. Other methods have been developed which can provide more accurate results, and the reader can continue the research.
For any comment or question, join the Facebook group and the Google+ Community about the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin.